Gst-NvDsUcx#
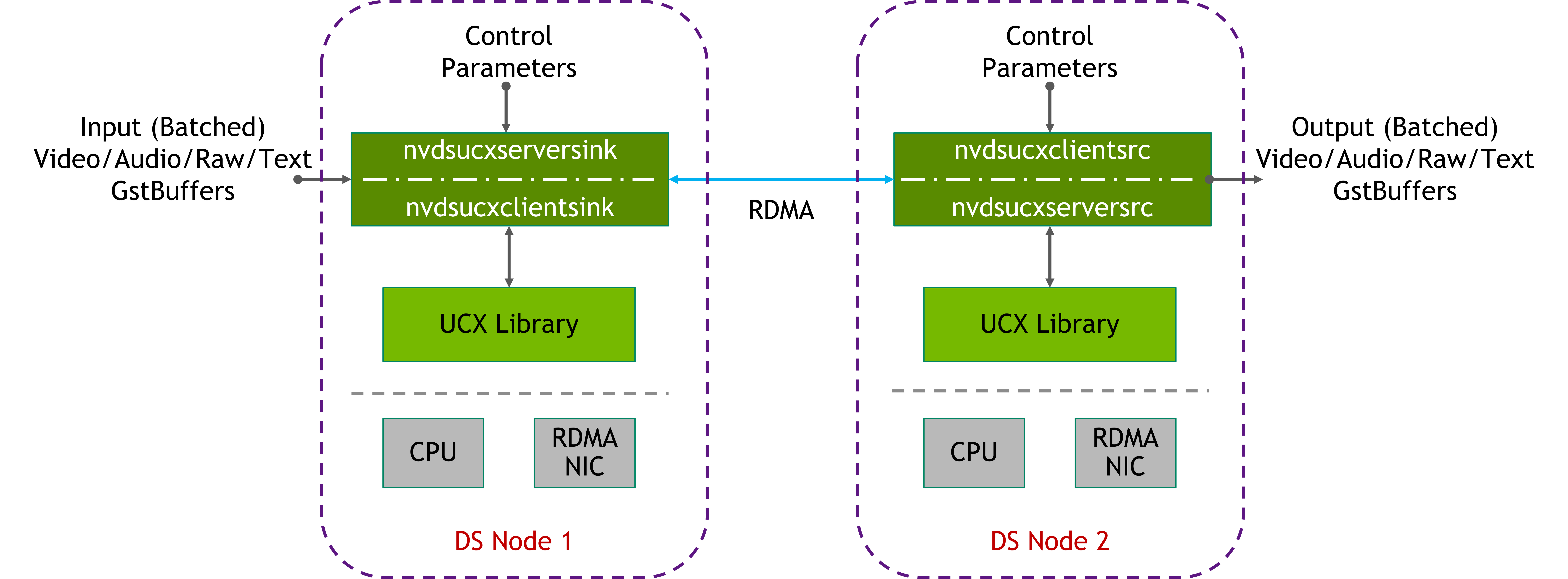
Gst-NvDsUcx is a Gstreamer plugin that provides a set of elements that can be used to send and receive pipeline data using RDMA. This allows for distributing the Gstreamer pipeline to various hosts in order to use distributed GPU resources. It is built on top of the Unified Communication X (UCX) library to send/receive Gstreamer packets over an RDMA-enabled network. UCX is an open-source library that accelerates data over high-performance networks and can utilize GPUDirect RDMA technology for minimal network latencies and highest throughput of distributed GPU traffic. For more details on UCX, see https://openucx.org.
Description#
Gst-NvDsUcx provides separate sink (to receive data from the pipeline) and source elements (to forward data to the pipeline), which connect to each other over the RDMA network. Furthermore, each sink or source type element can be a server or client, where the server element must be started before the client. As a result, the Gst-NvDsUcx plugin provides 4 elements: nvdsucxserversink, nvdsucxclientsink, nvdsucxserversrc, nvdsucxclientsrc.
Since the Gst-NvDsUcx plugin needs to present itself as a sink and source to the Deepstream pipeline, you need to pair the elements based on which part of the pipeline needs to be started first:
nvdsucxserversink<->nvdsucxclientsrc(Sink side starts first)nvdsucxclientsink<->nvdsucxserversrc(Source side starts first)
Requirements#
The Gst-NvDsUcx plugin has the following requirements (in addition to the Deepstream SDK requirements):
NVIDIA ConnectX6-DX NIC or later.
For more information on installing and configuring NICs, see: https://docs.nvidia.com/networking/display/ConnectX6VPI/Introduction
Install doca all package from https://developer.nvidia.com/doca-downloads?deployment_platform=Host-Server&deployment_package=DOCA-Host&target_os=Linux
UCX - version 1.13 or later - needs to be compiled with CUDA support or use CUDA-enabled UCX packages from the git repository directly, see openucx/ucx
For installation instructions, follow the Release build instructions from here: openucx/ucx. Note that UCX library should be compiled with CUDA as follows:
$ ./contrib/configure-release --prefix=/install/path --enable-examples --with-java=no --with-cuda=/path/to/cuda --enable-mt
Docker container support
If you wish to use the plugin inside a container, make sure to add the following flags during
docker runcommand:--privileged --network host--cap-add CAP_SYS_PTRACE --shm-size="8g"--device=/dev/infiniband/uverbs0--device=/dev/infiniband/rdma_cm--ipc=host-e CUDA_CACHE_DISABLE=0-v /dev/infiniband:/dev/infiniband
For additional metadata processing, Gst-NvDsUcx depends on the serialization library provided by the Gst-NvDsMetaUtils plugin.Refer to the Gst-NvDsMetaUtils documentation for configuring and installing the serialization library.
Note
This plugin is only supported on x86_64 platforms.
Inputs and Outputs#
Inputs (for Nvdsucxserversink or Nvdsucxclientsink)
Any one of the following:
NV12/RGBA NVMM Gst Buffer + (NvDsBatchMeta + Serialized NvDsUserMeta/Gst Meta - optional)
NVMM or Raw Audio Buffers + (NvDsBatchMeta - optional)
Raw Text Gst Buffers
Control parameters
addr
port
buf-type
gpu-id
raw-buf-size
nvbuf-memory-type
num-nvbuf
nvbuf-batch-size
num-conns
Output (from Nvdsucxserversrc or Nvdsucxclientsrc)
Any one of the following:
NV12/RGBA NVMM Gst Buffer + (NvDsBatchMeta + Serialized Video NvDsUserMeta/Gst Meta - optional)
NVMM or Raw Audio Buffers + (NvDsBatchMeta + Serialized Audio NvDsUserMeta/Gst Meta - optional)
Raw Text Gst Buffers
Gst Properties#
The Gst-nvdsucx plugin has the following properties based on which type of element is used:
Gst-nvdsucx gst properties# Property
Type of Element
Description
Type and Range
Examples
addr
Server
The IP address to which a client will connect
String
Default: 127.0.0.1
addr = 192.168.100.1
addr
Client
The server IP address
String
Default: 127.0.0.1
addr = 192.168.100.1
port
Server
Listening port for connections from clients
Integer 0 - 66535
Default: 7174
port = 4000
port
Client
The server port number
Integer 0 - 65535
Default: 7174
port = 4000
buf-type
All
Type of data handled by UCX:
0 - video
1 - audio
2 - raw-audio
4 - text
Default: 0
Integer
buf-type = 0
gpu-id
Source
GPU ID to use
Integer 0 - 4294967295
Default: 0
gpu-id=0
raw-buf-size
All
Size of raw buffer to allocate
Integer 0 - 8192
Default: 8192
raw-buf-size=1024
nvbuf-memory-type
Source
Type of NvBufSurface Memory to allocate for output buffers
0 - Default memory
1 - cuda-pinned (Allocate Pinned/Host Cuda Memory)
2 - cuda-device (Allocate Device cuda Memory)
3 - cuda-unified (Allocate unified cuda memory)
Default: 3
Integer
nvbuf-memory-type = 2
num-nvbuf
Source
The number of Nv Buffers to allocate
Integer 0 - 10
Default: 4
num-nvbuf = 8
nvbuf-batch-size
All
The maximal batch size of a Nv Buffer
Integer 1 - 2147483647
Default: 1
nvbuf-batch-size = 4
num-conns
ServerSink
The number of client connections to expect [1]
Integer 1 - 4
Default: 1
num-conns = 2
Footnote
Examples#
The DeepStream SDK 6.1+ includes three examples on how to use the Gst-NvDsUcx plugin to disaggregate/divide the Gstreamer pipeline to run on separate processes/servers. Note that each example has a server and client program to run different parts of the pipeline separately. Always start the server program before the client program.
Example 1:
The example here shows how to send/receive video data in the Gstreamer pipeline using serversink and clientsrc elements of the Gst-NvDsUcx plugin. The pipeline uses the uridecodebin and the nvvideoconverter plugins to pass the video frames to the serversink element based on the caps filter. The serversink forwards this video data to the clientsrc element (on another node/process using RDMA), which then forwards the data to the video converter. Finally, the data is stored in a file after encoding.
On DS Node 1:
gst-launch-1.0 uridecodebin uri="file:///sample_1080p.mp4" async-handling=1 name=src1 src1. ! \
queue ! nvvideoconvert ! 'video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080' ! \
nvdsucxserversink addr=192.168.100.1 port=4000 buf-type=nvdsucx-buf-video
On DS Node 2:
gst-launch-1.0 nvdsucxclientsrc addr=192.168.100.1 port=4000 nvbuf-memory-type=2 num-nvbuf=4 buf-type=nvdsucx-buf-video ! \
'video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1' ! \
queue ! nvvideoconvert ! nvv4l2h264enc ! h264parse ! qtmux name=mux_0 ! \
filesink sync=1 async=0 qos=0 location=~/out_1080p.mp4
Example 2:
This example shows how to distribute the DS pipeline using Gst-NvDsUcx plugin and use serialization / de-serialization components to send serialized data over RDMA network. The Deepstream pipeline here consists of the streammux plugin that takes input from the filesrc after decoding. The streammux passes the frames to the nvinfer plugin that identifies certain objects in the frames and add that metadata to the frame. The serialization plugin (part of the Gst-NvDsMetaUtils library) creates a binary object corresponding to the metadata and adds it to the frame. The clientsink and serversrc elements are used here to demonstrate the flexiblity of setup of the Gst-NvDsUcx here. The clientsink will send the additional metadata along with the video frame via RDMA to the serversrc.
The serversrc then forwards the data to the deserialization plugin which extracts it to append the metadata correctly to the frame. The nvdsosd plugin interprets the metadata (bounding boxes) and then the file is stored after encoding.
On DS Node 1:
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=~/sample_1080p.mp4 ! qtdemux ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! m.sink_0 nvstreammux name=m batch-size=1 ! \
nvvideoconvert ! nvinfer config-file-path=/opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-6.1/samples/configs/deepstream-app/config_infer_primary.txt ! \
nvdsmetainsert serialize-lib = "/opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-6.1/lib/libnvds_video_metadata_serialization.so" ! \
nvdsucxclientsink addr=192.168.100.1 port=4000 buf-type=nvdsucx-buf-video
On DS Node 2:
gst-launch-1.0 nvdsucxserversrc addr=192.168.100.1 port=4000 nvbuf-memory-type=2 num-nvbuf=8 buf-type=nvdsucx-buf-video nvbuf-batch-size=1 ! \
'video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1' ! nvvideoconvert ! \
nvdsmetaextract deserialize-lib = "/opt/nvidia/deepstream/deepstream-6.1/lib/libnvds_video_metadata_serialization.so" ! \
nvdsosd ! nvvideoconvert ! nvv4l2h264enc ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=~/out_1080p.mp4
Example 3:
This example demonstrates how audio data in a DS pipeline can be distributed across processes or nodes using the Gst-NvDsUcx and the Audio metadata serialization (part of Gst-NvDsMetaUtils) plugins. The streammux plugin interprets the audio data from the audio plugins and forwards it to the Gst-NvDsUcx plugin. Similar to the video metadata serialization plugin in Example 2, the audio metadata serialization plugin creates a binary object which the serversink element forwards to the clientsrc element. The audio metadata is extracted and added to the buffer for downstream plugins to interpret.
The streammux and streamdemux plugins only support audio in the new versions, so an environment variable must be set before the example is run.
On DS Node 1:
USE_NEW_NVSTREAMMUX=yes gst-launch-1.0 uridecodebin uri="file:///sample_1080p_h264.mp4" ! audioconvert ! \
audioresample ! 'audio/x-raw,format=F32LE,rate=48000,channels=1,layout=interleaved' ! audiobuffersplit ! \
a_streammux.sink_0 nvstreammux name=a_streammux batch-size=1 sync-inputs=1 max-latency=250000000 ! \
nvdsmetainsert serialize-lib="libnvds_audio_metadata_serialization.so" ! \
nvdsucxserversink addr=192.168.100.2 port=4000 sync=1 async=0 buf-type=nvdsucx-buf-nv-audio
On DS Node 2:
USE_NEW_NVSTREAMMUX=yes gst-launch-1.0 nvdsucxclientsrc addr=192.168.100.2 port=4000 nvbuf-memory-type=2 num-nvbuf=4 buf-type=nvdsucx-buf-nv-audio ! \
'audio/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=F32LE,rate=48000,channels=1,layout=interleaved' ! \
nvdsmetaextract deserialize-lib = "libnvds_audio_metadata_serialization.so" ! nvstreamdemux name=asd asd.src_0 ! \
audioconvert ! "audio/x-raw,format=S16LE" ! wavenc ! filesink sync=0 async=1 qos=0 location=out.wav